Warts: A Common Dermatological Encounter for Many
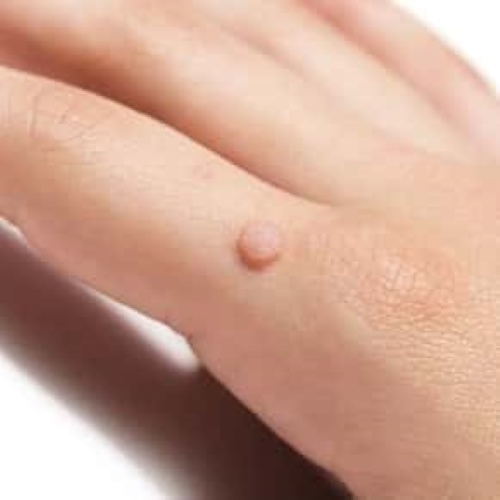
Skin warts are non-cancerous growths on the skin caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV infects the top layer of the skin, usually entering through a cut or abrasion. Warts can appear anywhere on the body, and their appearance varies depending on the type of HPV involved. Common types of warts include:
- Common Warts: These typically appear on the fingers, hands, and elbows. They have a rough, raised surface and may have black dots, which are small, clotted blood vessels.
- Plantar Warts: Found on the soles of the feet, plantar warts can be flat or grow inward due to pressure from walking. They may cause discomfort or pain, especially when walking.
- Flat Warts: These are small, smooth warts that often appear in clusters on the face, neck, hands, or knees. They are more common in children and teens.
- Filiform Warts: These warts have thread-like projections and often appear on the face, especially around the mouth, eyes, or nose.
- Genital Warts: These warts appear on or around the genital and anal areas. They are sexually transmitted and are caused by certain strains of HPV.
Warts are usually harmless and may disappear on their own over time. However, some may persist or spread, causing discomfort or cosmetic concerns. Over-the-counter treatments, such as salicylic acid or freezing agents, can be used to remove warts. In-office procedures performed by healthcare professionals, like cryotherapy (freezing), laser therapy, or surgical removal, may be recommended for stubborn or recurrent warts.
Skin warts are relatively common, and many people will experience them at some point in their lives. The prevalence of warts can vary by age, with certain types of warts being more common in specific populations. Here are some key points about the commonality of skin warts:
- Common Occurrence: Warts are one of the most common dermatological conditions. They can affect people of all ages, but children and teenagers tend to be more susceptible.
- Prevalence in Children: Warts are particularly common among school-aged children, with estimates suggesting that up to one in three children may develop warts at some point.
- Decline with Age: The incidence of warts tends to decrease with age. While they are common in children, older individuals may still experience warts, especially if they have factors that make them more susceptible.
- Weakened Immune System: People with weakened immune systems, whether due to medical conditions or medications, may be more prone to developing warts or experiencing more persistent cases.
- Common Types: Common warts, plantar warts, and flat warts are among the most frequently encountered types. Genital warts, caused by specific strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), are also common but are usually transmitted through sexual contact.
- Self-Limiting: Many warts are self-limiting, meaning they may resolve on their own without treatment. However, some warts can be more persistent and may require intervention.
It’s essential to note that while warts are generally harmless, they can be bothersome or cosmetically undesirable. Seeking medical advice for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment is recommended, especially if the warts are causing discomfort, spreading, or if there are concerns about their appearance.
It’s important to note that self-diagnosis and treatment may not always be effective, especially for genital warts, and consulting with a healthcare professional is advised. Additionally, preventive measures such as practicing good hand hygiene and avoiding contact with warts can help reduce the risk of HPV transmission.








